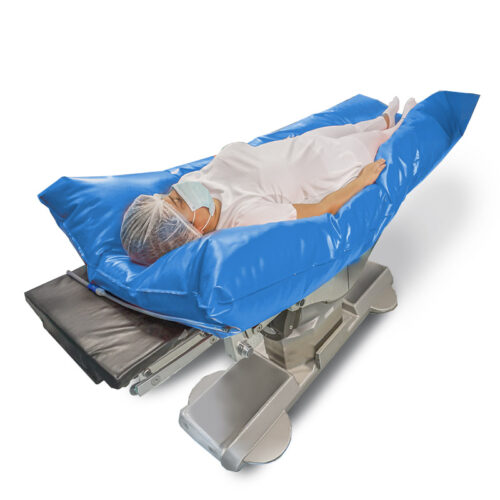
Operating Room Patient Positioning Solutions
This range offers versatile and efficient solutions for the patients’ positioning in the Operating Room during medical procedures .
Positioning Systems for the Operating Room
Positioners line for patients and operators’ comfort
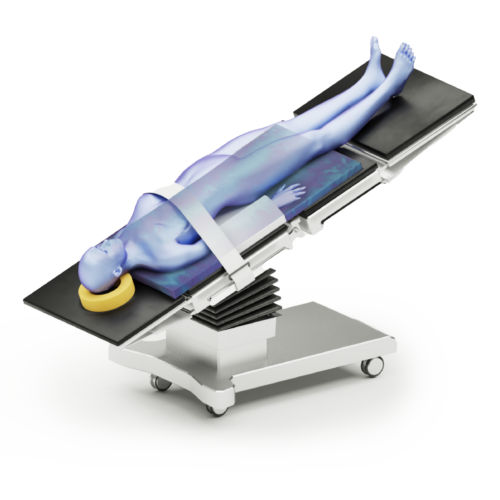
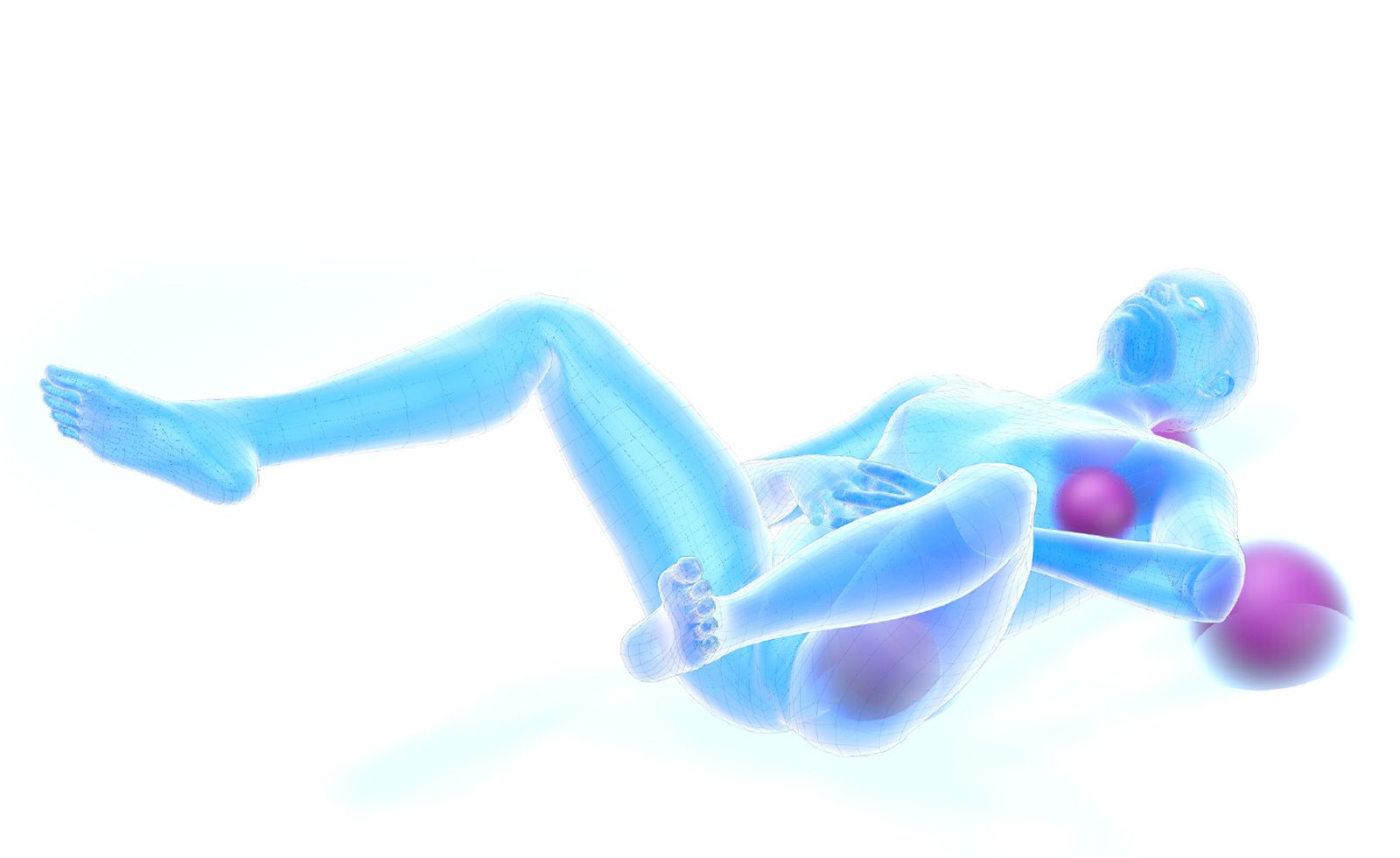
Supine Position
ATTENTION! Do not let feet protrude from the table to avoid compression or injuries of the Peroneal nerve or the Achilles tendon.

Recommended positioners:







Gynecological Position
CAUTION. The perineal area must overhang the table top by about 3-5 cm. in order to perform the procedure.

Recommended positioners:





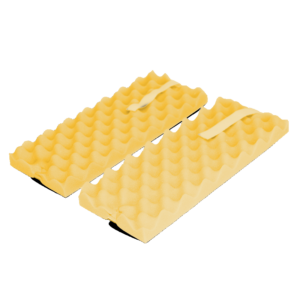




Lateral Decubitus Position
ATTENTION! The arm holder (lower arm) should not exceed an angle of 90° to the body. Flexion is applied differently depending on the surgery to be performed.
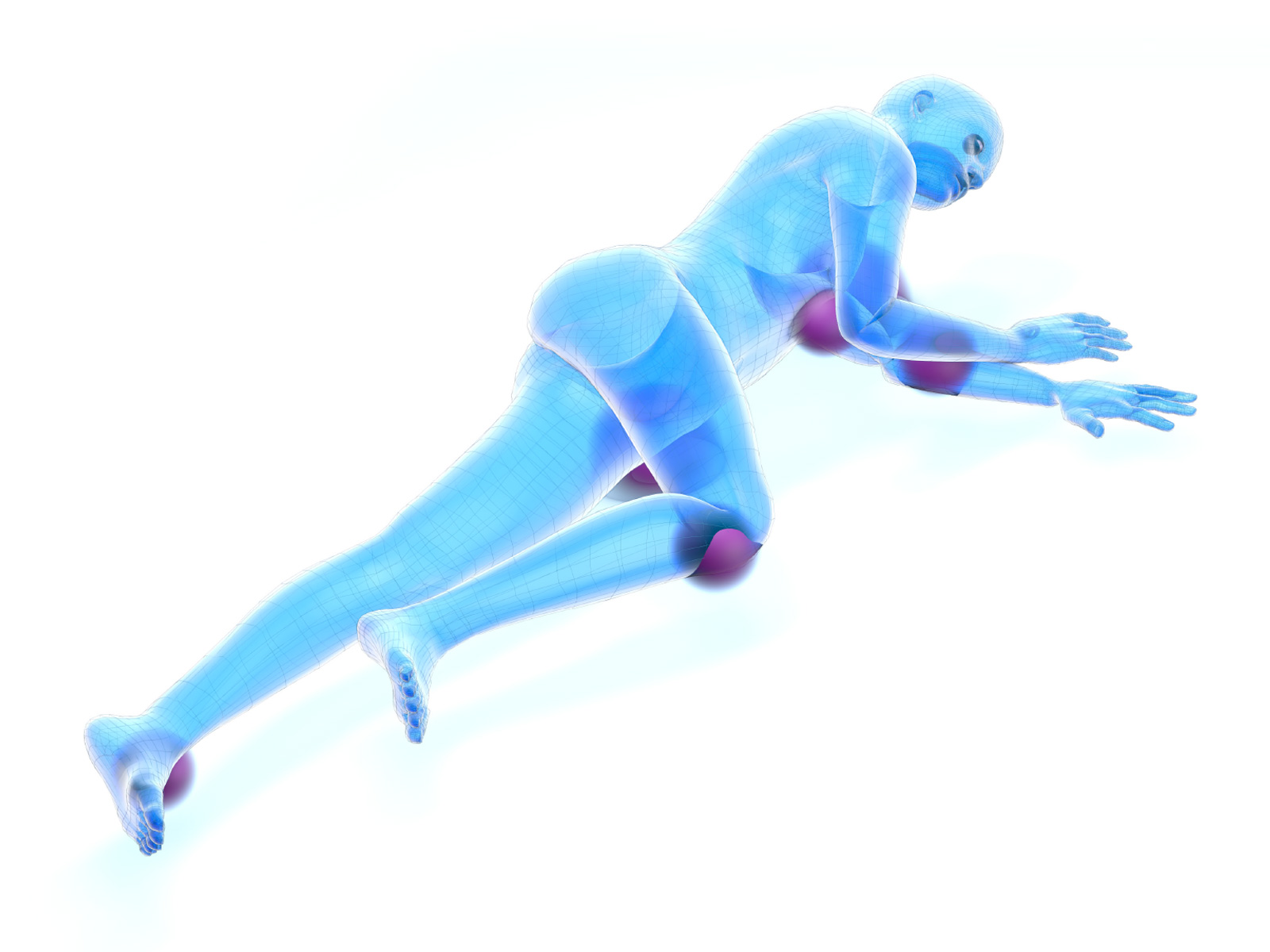

Recommended positioners:





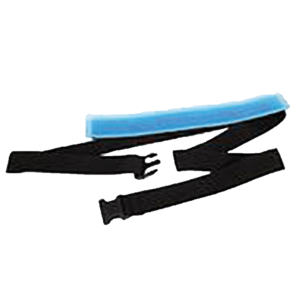






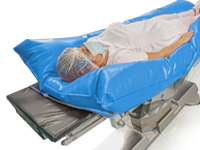
Prone Position
This position allows surgical access to the spine and the back of the head.
ATTENTION! The head must be aligned with the rest of the body and the face positioned on a suitable device that allows the intubated area to be left free.
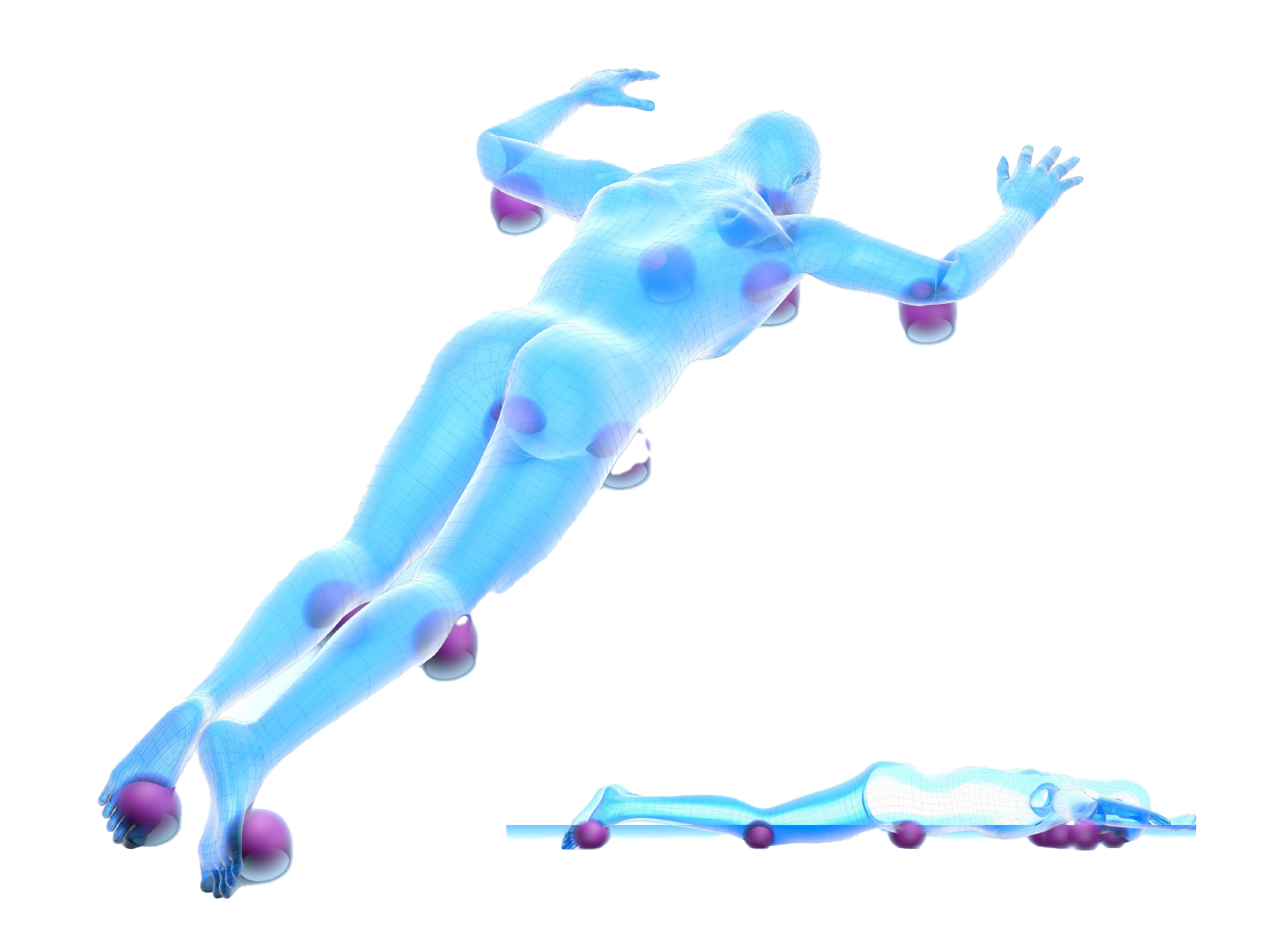

Recommended positioners:







Type of intervention or Surgery tecnique
After studying the case, the surgeon, and the team, define the optimal position considering the specific patient’s conditions.
Anatomical area to be treated
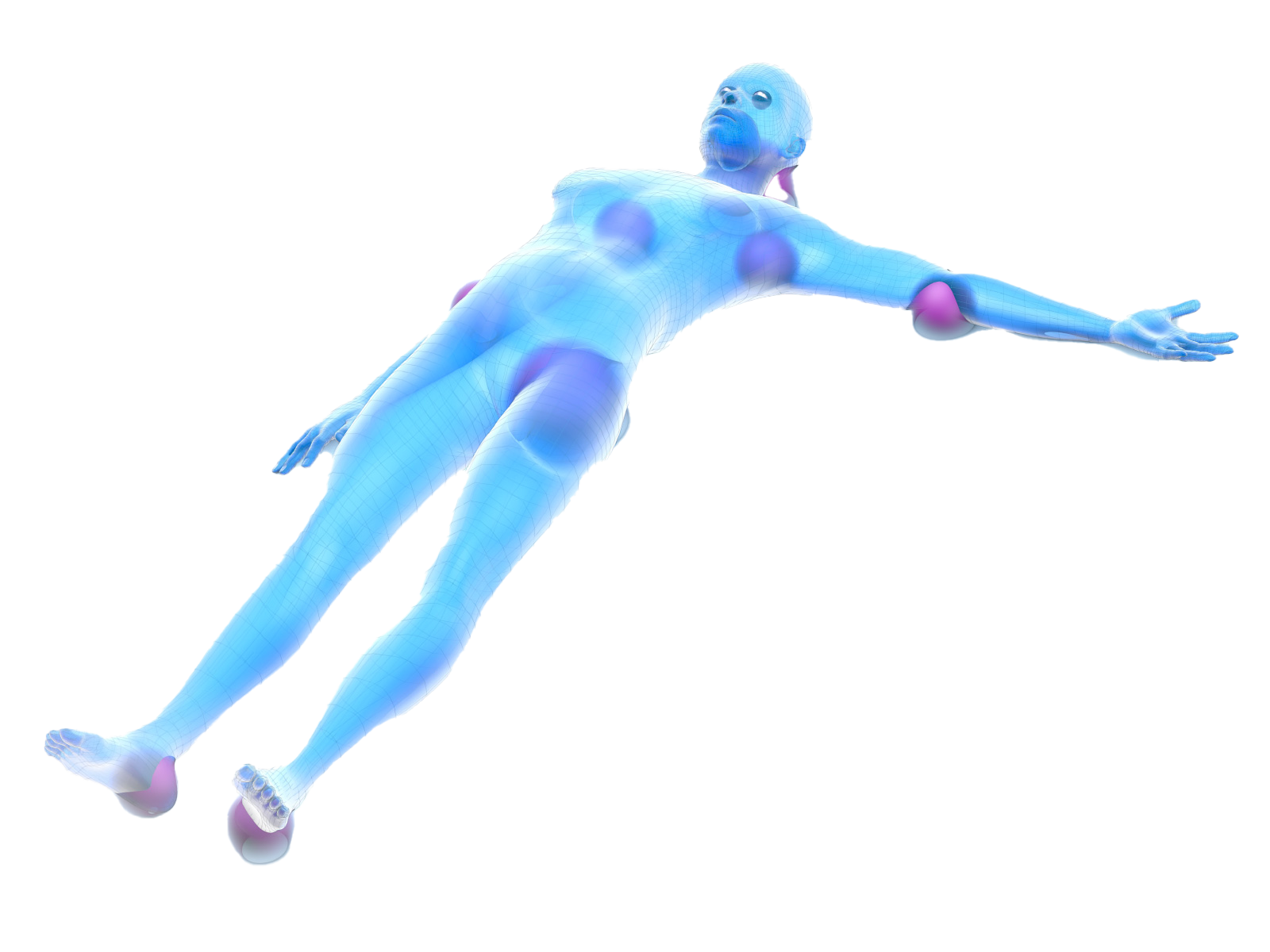
Depending on the localization of the intervention, it is possible to prefer various types of positioners. Size, conformation, and type of positioner can be determined not only by the district to be treated, but also by the anthropometric characteristics of the patient. It is also essential to consider the potential pressure damage to areas not directly affected by the surgical activity.
Type of material and positioner
Finally, the duration of the intervention, the level of comfort required, the type of practices and the tools used to verify the compatibility of materials are considered.